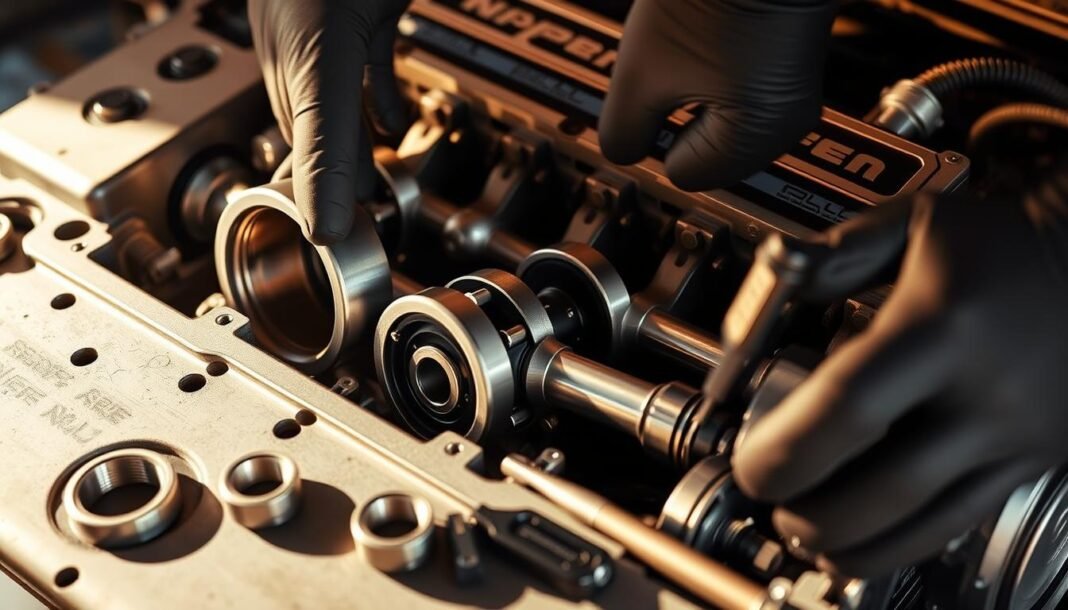
Replacing rod bearings in the 3.2L VR6 requires precision to avoid costly engine damage. This guide simplifies the DIY rod bearing replacement process, focusing on OEM procedures to ensure reliability. Proper marking of bearing caps, surface cleaning, and accurate torque settings are critical for long-term performance.
Key Takeaways
- Mark each bearing cap to maintain original orientation and prevent misalignment.
- Clean all bearing surfaces thoroughly to eliminate debris before installation.
- Follow torque specs: 30 Nm (22 ft-lbs) plus 90° rotation for connecting rod bolts.
- Use Plastigage to check bearing clearances during the DIY rod bearing replacement process.
- Replace bolts and nuts when removed to ensure proper clamping force.
Overview of the 3.2L VR6 and Rod Bearing Replacement Process
The 3.2L VR6 engine combines two rows of cylinders in a compact layout, making it a hallmark of Volkswagen engineering. This inline-V design balances power and space efficiency in vehicles like the Passat and CC. Before diving into repairs, grasp how its components interact.
Understanding the VR6 Engine Layout
VR6 engines rely on precise alignment between crankshaft rods and bearings. Key components include:
- Crankshaft: Converts piston movement into rotational force
- Connecting rods: Link pistons to the crankshaft
- Bearing caps: Secure bearings to the engine block
Manufacturers mark bearing caps with alignment codes to ensure correct installation. Misalignment here can cause catastrophic failure. Use this reference chart to avoid errors:
| Component | Function | Key Check |
|---|---|---|
| Rod bearings | Reduce friction between rods and crankshaft | Measure clearance with feeler gauges |
| Bearing caps | Secure bearings in place | Verify cap markings match engine block |
Importance of Proper Rod Bearing Replacement
“Incorrect bearing clearance can lead to premature wear or catastrophic engine failure.” – Volkswagen Service Manual
Improper installation risks metal-on-metal contact between rods and crankshafts. This causes overheating and scoring, costing thousands in repairs. Always follow these steps:
- Inspect crankshaft journals for scoring
- Reuse OEM bearings for proper tolerances
- Apply clean engine oil during reassembly
Regular inspections prevent costly surprises. Prioritizing precision here extends engine life by decades with proper care.
Necessary Tools and Materials
Replacing rod bearings in the 3.2L VR6 requires precise tools and materials to ensure proper 3.2L engine maintenance. Skipping even one item could lead to misalignment or damage. Gather everything before starting to avoid mid-job disruptions.
Essential Tools
- Socket set: A 3/8-inch or 1/2-inch set with deep sockets for tight spaces.
- Rubber mallet to gently tap components without scratching metal surfaces.
- Crankshaft socket for accessing hard-to reach bolts on the crankshaft.
- Breaker bar for loosening rusted or tight bolts.
- Feeler gauges to measure bearing clearances accurately.
- Plastigage: A critical tool for checking bearing clearances without a micrometer.
- Wire brush to clean oil passages and remove carbon buildup.
- 3/8-inch rubber hose to protect cylinder walls during bearing removal.
- Torque wrench to follow factory specifications during reassembly.
Additional Materials You’ll Need
Cleaning supplies are as vital as tools. Use hot soapy water to soak parts before cleaning. Include:
- Compressed air to dry components and blow out debris.
- Clean shop rags for wiping down parts post-cleaning.
- New rod bearings and engine oil for reassembly.
- Lubricating grease for threads and surfaces to ease reinstallation.
Organize all items on a clean work surface. Missing even one component delays progress and risks errors in 3.2L engine maintenance.
Preparing Your Workspace and Safety Guidelines
Before starting rod bearings installation, a well-organized workspace and strict safety practices are critical. This ensures accuracy and protects both you and the engine components. Proper setup prevents contamination and reduces the risk of costly mistakes.
“A cluttered workspace doubles the chance of oversight during delicate procedures like rod bearings installation,” warns the ASE Engine Repair Manual.
Setting Up the Work Area
- Mount the engine in a sturdy stand (e.g., VP Racing or Peak Engine Stands) to keep it stable and accessible.
- Use LED work lights to eliminate shadows when accessing tight engine compartments.
- Spread clean cloths over the work surface to catch debris and isolate parts during rod bearings installation.
- Store tools in labeled trays to avoid misplacement—keep torque wrenches and micrometers within reach.
Essential Safety Precautions
- Wear safety glasses and nitrile gloves to guard against lubricants and sharp metal edges.
- Secure a Class B fire extinguisher nearby—engine oil and solvents require vigilance.
- Never skip torque specs: Over-tightening during rod bearings installation can fracture bearings permanently.
- Use lifting straps for heavy engine blocks to prevent back injuries—always lift with legs, not the back.
Pro tip: Photograph each disassembled section before removing parts. Visual records help during reassembly after rod bearings installation. Stay focused—this phase sets the foundation for every step ahead.
Initial Steps: Accessing the Rod Bearings
Before reaching the rod bearings, start by draining the engine oil. Disconnect the battery and remove the valve covers to access the cylinder block. Use a floor jack to lift the engine slightly, securing it with jack stands for stable access. Clean the exterior with a degreaser to expose mounting bolts.

- Unbolt and remove the oil pan to expose the crankshaft. Inspect the pan gasket for debris that could obstruct engine lubrication pathways.
- Loosen cylinder head bolts in the recommended sequence to avoid warping. Document each bolt position for precise reinstallation.
- Clean oil passages with compressed air to remove particles. Clogged passages can disrupt engine lubrication, causing premature bearing wear.
- Mark bearing cap positions with a permanent marker. Number each cap and rod assembly to maintain proper alignment during reassembly.
- Secure the crankshaft with a vise using protective padding. Avoid overtightening to prevent surface damage.
Properly cleaning oil passages ensures consistent engine lubrication after reassembly. Misaligned bearings or unclean passages can lead to oil starvation, so double-check each step. Store removed fasteners in labeled containers to avoid confusion later.
how to replace rod bearings in 3.2l vr6
A mechanic guide for this task prioritizes precision. Start by cleaning old bearing surfaces with a wire brush to remove debris. Apply engine oil evenly to new bearings before installation to ensure smooth movement.
Step-by-Step Process Breakdown
- Position the bearing shells into their respective caps, aligning oil holes precisely. Mismatched holes block lubrication flow.
- Tighten main and rod caps in the factory-recommended sequence, using a torque wrench. Over-tightening warps the block.
- Rotate the crankshaft after each cap installation to check for binding. Resistance indicates improper fitment.
Key Techniques for Success
- Use a dial bore gauge to confirm bearing clearance. Aim for 0.001–0.002 inches for optimal performance.
- Wipe excess oil from mating surfaces to prevent contamination during reassembly.
- Verify all bolts reach specified torque values using a calibrated wrench. Specs vary by manufacturer—refer to service manuals.
Patience ensures longevity. Each step in this mechanic guide builds toward a properly sealed, balanced engine. Skip shortcuts to avoid costly rework.
Disassembling the Engine Components
Before tackling DIY rod bearing replacement, clear the workspace by removing parts blocking access to the rod bearings. Precision here ensures smooth progress through later steps. Use this phase to identify and set aside components systematically.
Removing Interfering Parts
Start by disconnecting electrical sensors and brackets attached to the cylinder block. Use a socket set to unbolt sensor wheels and mounting hardware. Record their locations using a notepad or smartphone photos. Key steps:
- Unplug engine sensors and label wires with zip ties.
- Remove valve cover and timing chain tensioner to expose crankshaft.
- Loosen bolts securing the oil pump housing, then lift it away from the block.
Organizing Components for Reassembly
Adopt a DIY rod bearing replacement strategy by creating a parts map. Use the table below to track bearings, rods, and caps:
| Component | Identification Method |
|---|---|
| Connecting rods | Metal tags with sequence numbers |
| Bearing caps | Sharpie markings on cap edges |
| Main bearings | Cloth pouches labeled by crankshaft position |
Place all bolts in muffin tins by size. Photograph each disassembly stage to cross-reference during reassembly. A clean workspace reduces rework later.
Installing New Rod Bearings Correctly
Proper installation of new rod bearings ensures your VR6 engine runs smoothly for years. Begin by cleaning the crankshaft journals and bearing bores thoroughly to remove all debris. Even microscopic particles can disrupt bearing alignment and oil flow.
- Align the bearing shells so their oil grooves face the engine block’s oil passages. This directs lubricant directly to critical contact points.
- Lubricate bearings with engine oil before placing them in the block. This prevents metal-on-metal contact during initial rotation.
- Install bearings using a press to avoid damaging soft metal surfaces. Confirm each shell’s locating tangs snap into the block’s guide slots.
After placing bearings, rotate the crankshaft manually to check for smooth movement. Listen for grinding noises and feel for resistance. Verify clearances with a dial bore gauge to match factory specifications. VR6 engine manufacturers like Volkswagen specify tight tolerances—deviations here risk premature failure.
“Misaligned bearings cause uneven load distribution, leading to catastrophic engine damage.” — King Engine Bearings
Always follow factory manuals for torque specs and bearing part numbers. Use new crush washers and reassemble in the same rod/rod journal sequence for proper balancing. Post-installation, perform a dry assembly check before refilling the oil system.
Reassembling and Final Checks
After installing new rod bearings, reassembling the 3.2L VR6 requires methodical checks to guarantee reliability. Proper 3.2L engine maintenance depends on precise reassembly, ensuring every component aligns with factory guidelines.

“Improper torquing can lead to significant problems, especially when different materials are used in engine components.” – John Phennig, Navistar International Corp.
Verification of Proper Installation
Begin by confirming bearing clearance and axial play with feeler gauges. Ensure crankshaft spins freely by hand before closing the engine. Use a torque wrench to fasten bolts to factory specs:
| Component | Recommended Torque (ft-lbs) |
|---|---|
| Cylinder Head Bolts | 70-75 |
| Main Bearing Bolt | 135 |
Engine Testing Procedures
Test the engine in phases to avoid damage:
- Crank the engine manually to check for resistance. A stiff crank indicates misalignment.
- Start the engine and idle for 30 seconds. Listen for ticking (loose bearings) or knocking (improper clearances).
- Check oil pressure and inspect for leaks around gaskets and seals.
Document all measurements and compare results to manufacturer guidelines. Skipping these steps risks costly repairs down the line.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Encountering issues after rod bearings installation? This section highlights fixes for common mistakes. Spotting problems early ensures your engine runs smoothly.
Identifying Common Mistakes
Watch for these red flags during rod bearings installation:
- Improper bearing cap alignment causing misalignment
- Oil passage blockages from debris
- Over-tightened fasteners warping components
- Unmarked bearing caps swapped during reassembly
- Inadequate lubrication leading to premature wear
Solutions and Practical Fixes
Quick fixes for typical errors:
| Issue | Quick Fix |
|---|---|
| Loose bearing clearance | Measure clearances with a micrometer before assembly |
| Oil flow restrictions | Flush passages with solvent and compressed air |
| Incorrect torque specs | Follow factory torque sequence and values |
| Cap mix-ups | Mark each cap and rod pair with numbered tags |
Pro tip: Always double-check bearing cap alignment with a straightedge before final tightening. Lubricate mating surfaces with engine oil or molybdenum paste as specified in the manual.
Tips and Best Practices for DIY Mechanics
DIY engine work needs careful steps and smart planning. These tips help avoid mistakes and boost success:
- Use a marker to label each bearing cap. This keeps track of their exact positions during reassembly.
- Take photos at every stage. These act as a visual guide for puttinging parts back correctly.
- Follow OEM manuals closely. They give exact specs for torque and clearances.
- Use precision tools like micrometers. Accurate measurements prevent fitment issues.
- Study repair forums or videos. Watching experts helps you avoid common errors.
- Check engine lubrication quality. Use factory-recommended oils and greases for bearings and mating surfaces.
Always recheck measurements before starting the engine. Proper engine lubrication and clear steps protect your investment. Take your time—methodical work builds confidence and ensures long-term performance.
Post-Maintenance Care and Engine Performance
Proper post-replacement care ensures your VR6 engine runs smoothly for years. Follow this mechanic guide to maintain performance and prevent future issues.
Routine Inspections
- Check oil levels weekly and replace oil every 3,000–5,000 miles.
- Listen for unusual noises monthly; irregular knocks may signal bearing wear.
- Use a dial indicator yearly to verify rod bearing clearances.
Long-Term Maintenance Tips
| Maintenance Task | Frequency | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Oil Analysis | Every 10,000 miles | Identify metal particles indicating wear. |
| Cylinder Head Alignment | Every 5 years | Prevent bearing misalignment stress. |
| Professional Inspection | Every 2 years | Expert assessment of engine health. |
Follow this mechanic guide to track performance trends. Avoid over-tightening bolts during inspections—they should match factory torque specs. Record data in a maintenance log for easy reference. Regular checks turn potential problems into preventable ones.
Conclusion
DIY rod bearing replacement for your 3.2L VR6 demands precision and patience. Proper preparation ensures engine longevity by matching connecting rod caps to their correct positions. Skipping this step risks misalignment, leading to bearing wear and potential engine failure. Clean all components thoroughly before assembly to avoid debris-caused damage. Apply bearing assembly lube evenly to prevent dry starts and friction-related issues.
Using tools like a roll stake tri-roller swaging tool ensures bearings seat securely without material stress. Post-installation inspections and regular oil checks maintain performance. Neglecting these steps can undo hours of work, so follow each guide step-by-step. Proper storage of bearings and ongoing maintenance, like checking for leaks or noises, prolongs engine life.
DIY rod bearing replacement becomes manageable with the right approach. Trust the process: clean parts, precise tool use, and systematic checks build a reliable engine. Share this guide with fellow mechanics and keep refining your skills. A well-maintained VR6 rewards you with smooth power and confidence behind the wheel.